An inventory management system ensures that one knows what to stock up on or sell out before it is too late. Businesses, in turn, aim to bring down their inventory carrying costs by using these automated or manual systems, and yet they never seem to be satisfied with reducing the inventory to a certain level. In this guide, we will check out the different types of inventory management systems available in the market and how they work, with examples and advice on what functions to look out for when making a purchase.
What is an Inventory Management System?
This describes the processes you use to track your goods along your entire business supply chain—from purchase right through to sales of the end product. In essence, it’s a guideline for stock control for your business. Proper inventory management is an important issue that most companies that deal with warehousing need to consider.
Why You Need an Inventory Management System?
Any company that carries stock needs a system that can track and control that stock correctly. No matter how small or big, without one, things get done on an ad hoc basis, leading to overstocking or understocking.
Advantages of an Inventory Management System
Here are five of the most important reasons why you should have an inventory management system:
- Better Visibility in Your Inventory: Keeping an eye on all the inventory movements helps you know the stock in hand and gives you an idea of when you need to reorder the same.
- Meet Customer Demand: Never run out of stock again. Decrease the probability of losing a sale as you meet customer demands.
- Get to Know Your Profitability: Record all data of inventory to break up costs of sales and production, total inventory value, and informative information about profitability.
- Enhances Workflow Efficiency: Automate inventory tracking to eliminate the need for regular checking in order to optimize operations.
- Accurate Financial Reporting: Proper tracking of stock and purchases to monitor the true value and profitability of your business.
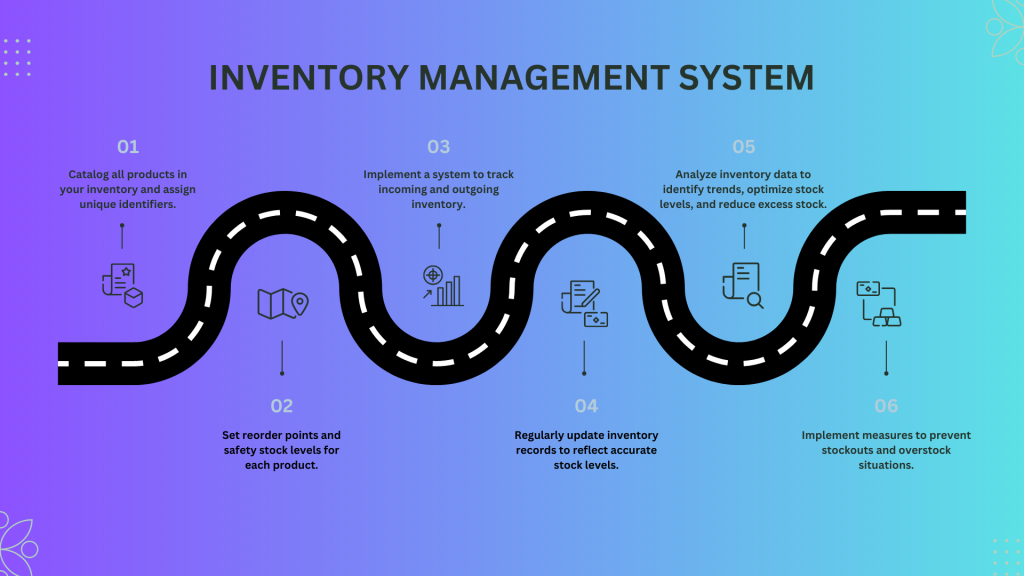
How an inventory management system works?
Online inventory management systems take updating the stock levels and tracking the inventories in the supply chain a step further. Other features include time purchasing, building products from a Bill of Materials, the capability to promise a customer order from multiple sales outlets, and the enhancement of many inventory control procedures.
Examples of Inventory Management Systems
Inventory management systems take many forms and functions. Some are really basic pen-and-paper or spreadsheet systems that require loads of manual data entry, while others are sophisticated software systems that can truly automate much of the inventory management process.
1. Simple Pen-and-Paper or Spreadsheet-Oriented Systems, with a Lot of Manual Data Entry:
Example: Priya and Ravi run a small book distribution godown. Priya has made a spreadsheet in Excel, which they update every time they need to order more stock. Ravi is in marketing, and when he sells a book, the same is reflected in the spreadsheet so that the update tells them the current stock level, reorder dates, etc.
2. Use of Basic Stock Management Software in a Local Retail Store:
Example: Every bit of truly basic functionality found in the accounting software Sarah’s Boutique is a clothes store that enables them to keep a track of their inventory and sales. Thus, the system lets them track inventory and sales in one place, but automated reordering and detailed features of analytics do not exist there.
3. Automated Systems in a Mid-Sized Manufacturing Company:
Example: AutoParts Co., a car parts manufacturer, uses an automated inventory management system to track components and finished products. This cloud-based system integrates business applications, increasing visibility across the organization. At the same time, it eliminates administrative tasks for operations and ensures that all necessary parts are always in stock.
4. Global Business with Cloud-Based System:
Example: GreenGadget Inc. – an electronics manufacturer. GreenGadget possesses a cloud software system that allows it to monitor its inventory in several warehouses. The software correlates e-commerce with the inventory, such that it updates the level of stock the moment goods are sold. This same system also allows it to prepare reports regarding historical data for its sales and forecasting for future demand and supplier availability. That is what gives GreenGadget Inc. the ability to make more timely purchasing decisions, conserve cash flow, and support growth.
5. Wholesale Distributor with Barcode Inventory System:
Example: FreshProduce Wholesale is a distributor of fresh fruits and vegetables with a barcode inventory system. This provides them with a follow-up on both the ins and outs of the stocks properly, minimizing errors, and offers them the highest level of efficiency in their order fulfillment process.
6. Small IT Firm Capable of Asset Inventory Management:
Example: Techie Solutions is a small IT services firm capable of using asset inventory management software. That way, it can itself buy the necessary equipment—laptops, servers, and other networking equipment—to satisfy the requirements of the purchasers.
7. Construction Company – Inventory Management System:
Example: BuildRight Construction monitors the materials it uses in building and tools needed in construction through a cloud-based inventory management system. This ensures that field requirement of materials is kept; hence, materials are available in different construction sites and prevents delays because of no stock.
8. Furniture Manufacturer – Warehouse Management System:
Example: CozyHome Furniture installed a warehouse management system to help organize, administrate, and enable optimization of its storage facility. It has simplified the management of raw materials and finished products, becoming more efficient and doing away with handling time.
Types of Inventory Management Systems
Periodic vs. Perpetual Inventory Systems
Learn how the two systems differ, and this will be helpful in determining the approach that suits your business. Each system has its unique benefits and methods of operation.
Periodic Inventory System
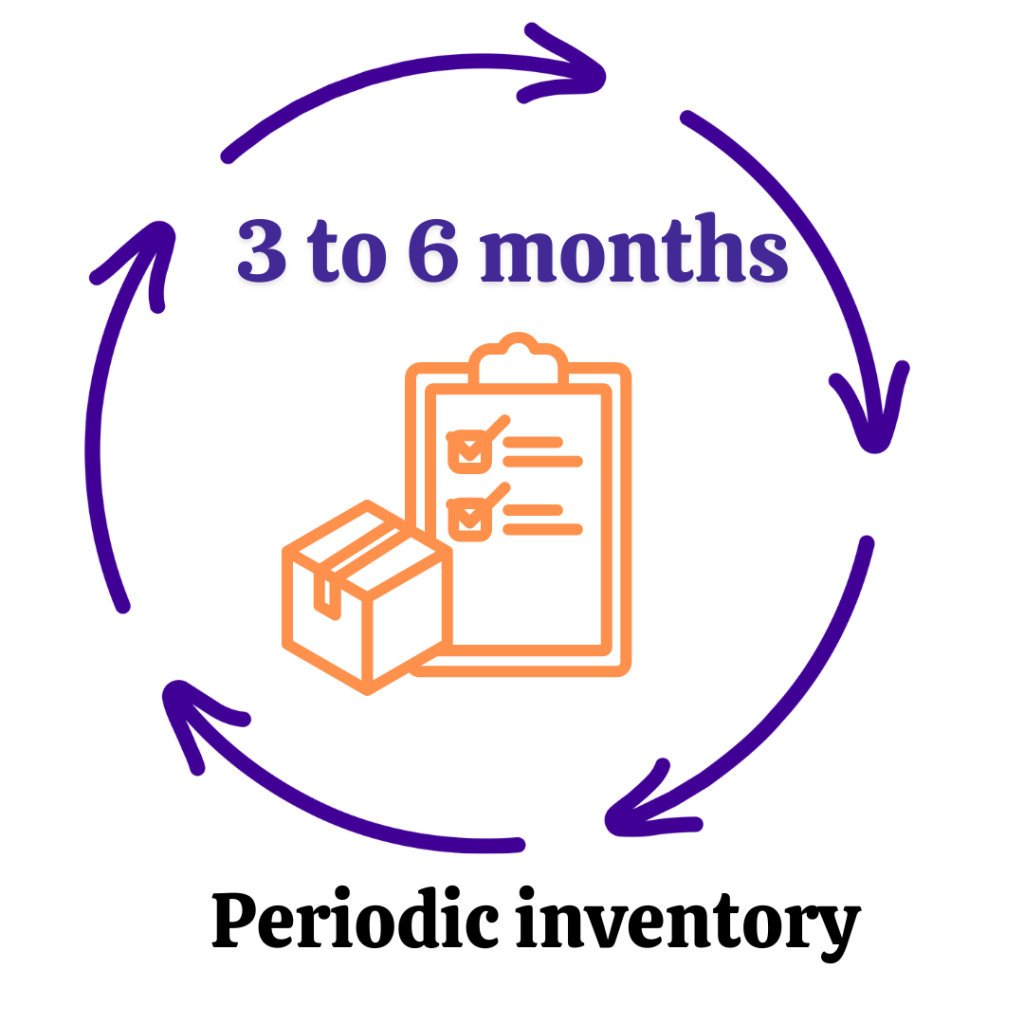
Regular Stock Counts of the Closing Stock
Detail: It depends upon the scheduled counting of the stock for verification of the accuracy of the inventory. Such counts usually occur every 3 to 6 months.
Advantages
- Cost-Effective: The hardware or software to implement the system is often lower since it does not need advanced technology.
- Simplicity: More comfortable to manage for small businesses that have less inventory or processing of fewer transactions.
Disadvantages
- Accuracy Issues: Inaccurate inventory data could lead to discrepancies and potential stockouts, given the long time periods between counts.
- Laborious: Largely human-based with regular physical counts that are highly intrusive.
Example of Periodic Inventory Management System:
Non-profit Organization with Periodic Inventory System:
Example: Charity Clothes is a non-profit organization of donating clothes to the deprived and homeless. They use a periodic inventory system by counting its stock every three months to ensure the inventory records match the actual stock in its possession.
Perpetual Inventory System

Continuous Tracking
Detail: The system continuously monitors the levels of stock as goods are received, produced, sold, or returned, providing current stock figures.
Advantages
- Real-Time Data: Gives up-to-date and accurate inventory levels. That would reduce the dependency on periodic stock takes.
- Efficiency: It improves the effectiveness of management of inventory since it enables better decisions for businesses from the acquired real-time data.
- Reduced Stock Discrepancies: Reduces the risk of stock discrepancies and increases the inventory accuracy overall.
Disadvantages
- Higher Initial Costs: Expensive technology and software systems for its implementation.
- Complexity: It is trickier to implement and manage, and often requires training and sometimes more advanced IT infrastructure.
Example of Perpetual Inventory Management System:
E-Commerce Growing Business with the Perpetual Inventory System:
Example: FitEtquip is a virtual retailer of fitness equipment. FitGear uses a perpetual inventory system that updates each time the products are received, sold, or returned. This system supports them to keep accurate stock levels while streamlining order fulfilment.

An inventory management system, or inventory management software, is essential for businesses to streamline tracking and controlling stock across the entire supply chain. This helps companies avoid overstocking and understocking, reducing costs and improving overall efficiency. Whether you opt for a simple system or a complex ERP solution, understanding the different types and their features will help you choose the best fit for your business needs. Costs can range widely, so it’s crucial to consider your specific requirements and the potential return on investment. Ultimately, an effective inventory management system will support your business growth and operational success.

